What is a Principal Balance on a Loan?
Contents
If you’re wondering what a principal balance is on a loan, you’re not alone. Many people don’t know what this term means, but it’s actually quite simple. A principal balance is the remaining amount of money that you owe on a loan, excluding any interest or other fees.
Checkout this video:
What is a Principal Balance?
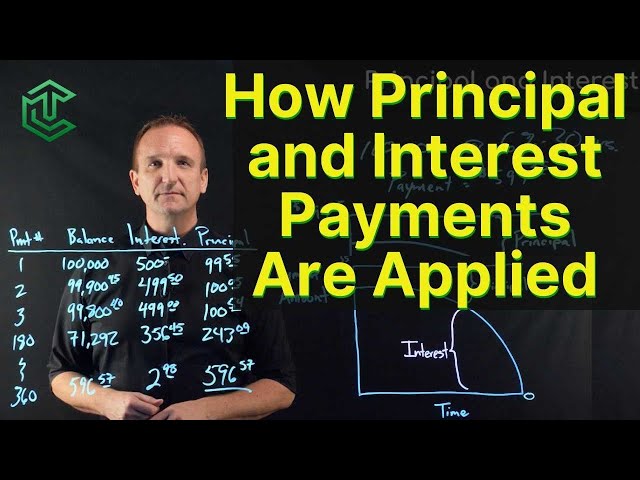
The principal balance of a loan is the remaining balance that you owe on the loan after making all scheduled payments up to a certain point in time. In other words, it’s the original loan amount minus any payments that have been made toward the loan.
For example, let’s say you take out a $10,000 loan with a 4% interest rate and a 10-year repayment term. Your monthly payment would be $103.38, and the total interest you would pay over the life of the loan would be $1,206.56. This means that your principal balance at the end of 10 years would be $8,793.44.
Your principal balance can go up or down depending on whether you make extra payments on your loan or if you miss scheduled payments. If you make extra payments, your principal balance will go down because you will have paid off more of the loan. However, if you miss payments, your principal balance will go up because you will still owe the full amount of the loan plus any accrued interest and late fees.
It’s important to know what your principal balance is because it affects how much interest you will pay over the life of the loan and how long it will take to fully repay the loan. If you want to pay off your loan as quickly as possible, you can make extra payments to reduce your principal balance faster and save money on interest payments in the long run.
How is a Principal Balance Determined?
The principal balance of a loan is the remaining amount that you owe on the loan, excluding any interest or fees. Your principal balance will go up if you make payments that don’t cover the full amount of your interest, and it will go down if you make payments that are more than the amount of your interest.
How Does a Principal Balance Affect Loan Repayment?
Your loan’s principal balance is the remaining amount you owe on your loan, not including interest or other fees. For example, if you take out a loan for $10,000 and have paid back $5,000, your principal balance is $5,000. Because the principal balance is the amount of money you borrowed minus what you’ve already paid back, it can decrease over time as you make payments—or it can increase if you choose to borrow more money or make late payments.
How Does a Principal Balance Affect Loan Repayment?
Your loan repayment schedule is based on your loan’s terms—the interest rate, repayment period, and whether you have a fixed-rate or variable-rate loan. To give you an idea of how your monthly payment might change as your principal balance decreases (or increases), let’s look at an example:
Assume you have a $50,000 fixed-rate loan with a 5% interest rate and a 10-year repayment period. Your monthly payment would be $592.86, and $50,000 would be your starting principal balance. According to this repayment schedule, after 10 years of making the same monthly payment, you would have paid off your entire loan and would owe nothing more.’;
$page_content = str_replace(‘##’, ‘
‘, $page_content); //Changes ## to
$page_content = str_replace(‘Heading:’, ‘
‘, $page_content); //Changes Heading: to
echo $page_content;
What Happens if the Principal Balance is Not Paid in Full?
If you have a loan with a principal balance, you are expected to pay that amount back in full. However, if you do not pay the entire balance, there are a few things that could happen.
The first is that you will be charged interest on the outstanding balance. This means that if you only make the minimum payment, a portion of your payment will go towards paying off the interest and the rest will go towards the principal. This also means that it will take longer to pay off the loan if you have a balance remaining.
The second thing that could happen is that your lender may require you to pay more each month until the balance is paid in full. This is because they want to make sure that they are getting their money back and not just the interest.
The third thing that could happen is that your lender may take legal action against you. This is usually a last resort, but it is something that could happen if you do not pay your loan back in full.
It is always best to try and pay off your loan in full so that you do not have to worry about any of these things happening. If you cannot afford to do this, then you should at least try and make extra payments each month so that you can reduce the balance as quickly as possible.
How to Pay Off a Principal Balance
The best way to pay off a principal balance on a loan is to make extra payments on the loan. When you make an extra payment on a loan, the money is applied to the principal balance of the loan. You can make an extra payment on your loan by sending in a check for the amount of the extra payment with a note that says “apply to principal”. You can also contact your loan servicer and tell them that you want to make an extra payment on your loan and specify that you want the payment to go towards the principal balance.