How Does a Loan Work?
Contents
Find out how a loan works before you apply for one. We’ll explain the different types of loans and what you need to know before you get one.
Loan Work?’ style=”display:none”>Checkout this video:
Introduction
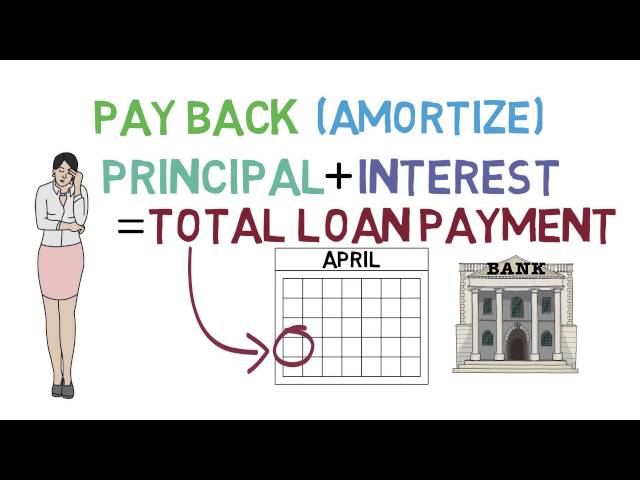
A loan is a type of debt. People usually take out loans to buy things that they cannot afford to pay for with cash, such as a car or a house. When you take out a loan, you agree to pay the lender back over time—usually in equal monthly payments. The lender gives you the money you need upfront and charges you interest (a percentage of the amount you borrow) until you repay the full amount of the loan.
What is a loan?
A loan is a debt provided by one party (the lender) to another party (the borrower) where the lender expects the borrower to repay the loan in full, with interest. The loan is generally repaid in installments, or payments, over a period of time. The term of the loan may be short-term, generally no more than a year, or long-term, often several years.
How does a loan work?
Taking out a loan is a big decision. You need to understand how loans work and what you’re agreeing to before you sign on the dotted line.
Loans are a form of debt that people use to finance big purchases or consolidate other debts. When you take out a loan, you’re borrowing money from a lending institution and agreeing to repay that money, plus interest, over a set period of time. The lender will give you the money you’ve requested, and you’ll make regular payments until the loan is paid off.
The terms of your loan will depend on the type of loan you’re taking out, as well as the lender’s policies. But in general, here’s how it works:
You’ll fill out an application with the lender, which will include information about your financial history and income. Based on this information, the lender will decide whether or not to approve your loan and, if so, how much money to lend you.
If you’re approved for the loan, you’ll sign a contract that outlines the terms of your agreement. This contract will include information like the interest rate (the amount of interest you’ll pay on the borrowed money), repayment schedule (how often and how much you’ll need to pay), and late payment fees (if any). Once you’ve signed the contract, the lender will give you the money you’ve requested.
You’ll then make regular payments until your loan is paid off. These payments will go toward both the principal (the borrowed money) and interest (the cost of borrowing that money). Depending on your loan terms, these payments may be monthly, biweekly, or even weekly.
The different types of loans
There are several types of loans, including personal loans, student loans, mortgages, auto loans, and more. Each type of loan has its own criteria for eligibility, terms, and repayment schedule.
Personal loans are typically unsecured, which means they are not backed by collateral like a house or a car. This makes them more difficult to qualify for than secured loans. Personal loans can be used for a variety of purposes, such as consolidating debt, paying for home improvements, or covering unexpected expenses.
Student loans are designed to help students pay for college. There are two types of student loans: federal and private. Federal student loans are provided by the government and have fixed interest rates. Private student loans are provided by banks and other financial institutions and have variable interest rates. Federal student loans have more generous repayment terms than private student loans.
Mortgages are loans used to finance the purchase of a home. The loan is secured by the home itself, which means that if the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can foreclose on the home and sell it to recoup their losses. Mortgage terms can vary greatly depending on the type of loan (fixed-rate or adjustable-rate), the length of the loan (15-year or 30-year), and the borrower’s credit history.
Auto loans are used to finance the purchase of a new or used vehicle. The loan is secured by the vehicle itself, which means that if the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can repossess the vehicle and sell it to recoup their losses. Auto loan terms also vary depending on factors such as the length of the loan (36 months or 60 months), the type of vehicle being purchased (new or used), and the borrower’s credit history.
The benefits of taking out a loan
There are many reasons why people take out loans, whether it’s to buy a car, consolidate debt, or finance a home improvement project. But what are the benefits of taking out a loan?
One of the biggest benefits of taking out a loan is that it can help you to make a large purchase that you might not be able to afford upfront. A loan can also help you to spread the cost of a purchase over a period of time, making it more affordable.
Another benefit of taking out a loan is that it can help you to improve your credit score. If you make regular, on-time payments on your loan, this will show up on your credit report and will help to improve your credit score. This can be helpful if you want to apply for other types of credit in the future, such as a mortgage or another loan.
Finally, taking out a loan can give you peace of mind in knowing that you have the funds available to cover an unexpected expense. If you have an emergency fund in place, this can help you to avoid taking out a high-interest loan or using a credit card to cover the cost.
The risks of taking out a loan
When you take out a loan, you’re borrowing money from a lender and agreeing to repay that money, plus interest, over a set period of time. Loans can come from banks, credit unions, or other financial institutions, or they can be funded by businesses or individuals.
Before you take out a loan, it’s important to understand the risks involved. When you borrow money and don’t repay it as agreed, you can damage your relationship with the lender, your credit score, and your ability to borrow money in the future. Make sure you can afford the payments and that you’re comfortable with the terms of the loan before you sign any paperwork.
How to repay a loan
Most loans must be repaid within a certain time frame, called the loan term. The loan term is the period of time during which you are required to make payments on your loan. The typical loan term is five to seven years, although some loans may have terms of one year or less.
At the end of the loan term, you will need to either pay off the remaining balance in full, or you may be able to refinance the loan and extend the term. If you choose to refinance, you will likely be required to pay closing costs and fees.
Conclusion
A loan is a sum of money that is borrowed and typically needs to be repaid with interest. There are many different types of loans, but they all work in essentially the same way: You borrow a certain amount of money and then agree to pay it back, usually in equal installments, over a set period of time. The interest rate on your loan will determine how much you end up paying in total.
There are many different factors to consider when taking out a loan, so it’s important to do your research and shop around before choosing a lender. It’s also important to make sure you can afford the monthly payments and that you will be able to repay the loan in full within the agreed-upon time frame.
If you’re considering taking out a loan, remember to ask plenty of questions and read all of the fine print before signing any paperwork.