How Does a Loan Work from the Bank?
Contents
How Does a Loan Work from the Bank? We take you through the process step by step so you can understand what’s involved in taking out a loan.
Checkout this video:
How a Loan Works
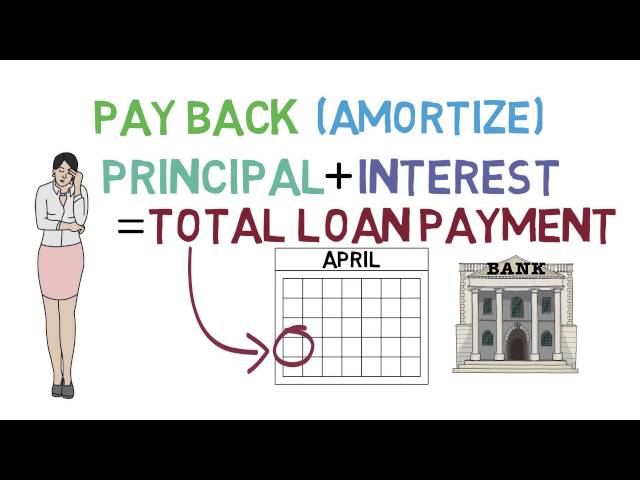
A loan is when a lender gives you money that you will need to pay back with interest. The amount of money that you borrow is called the principal. The interest is the fee that the lender charges for lending you the money. The interest rate is the percentage of the loan that you will need to pay back in addition to the principal.
Applying for a Loan
When you apply for a loan, the bank will review your financial history and credit score to determine if you are eligible for a loan and, if so, how much they are willing to lend you. The amount of money you are eligible to borrow is called your loan limit.
To apply for a loan, you will need to fill out a loan application form and provide the bank with information about your income, expenses, and debts. You will also need to provide the bank with some collateral, or something that the bank can use to secure the loan in case you default on the loan payments.
Once the bank has reviewed your application and determined that you are eligible for a loan, they will provide you with a loan agreement that outlines the terms of the loan, including the interest rate, monthly payments, and length of the loan. Once you have signed the loan agreement, the bank will disburse the funds to you in one lump sum.
The Loan Process
When you take out a loan, you agree to borrow a certain amount of money from a lender and to repay that money, plus interest, over a set period of time. The loan process usually starts with an application, followed by underwriting and, if everything goes well, funding.
The first step in the process is to fill out a loan application. This can be done online, over the phone, or in person at a bank or other lending institution. The applicant will usually be asked to provide some personal information, such as their name, address, and Social Security number, as well as information about their income and employment history. The lender will also need to know how much money the applicant wants to borrow and for what purpose.
Once the application is complete, it will be sent to the lender’s underwriting department for approval. The underwriters will review the application and supporting documentation to make sure that the borrower meets all of the eligibility requirements for the loan. They will also check the borrower’s credit history to determine whether they are likely to repay the loan on time. If everything looks good, the loan will be approved and funding can be issued. If there are any concerns, however, the underwriter may request additional information or documentation from the borrower or reject the loan outright.
Loan Types
There are many different types of loans available to consumers, and each type has its own pros and cons. Here is a brief overview of the most common types of loans:
Mortgage Loans: A mortgage loan is a loan used to purchase a home. The loan is secured by the home itself, so if the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can foreclose on the home and recoup its losses. Mortgage loans are typically repaid over a period of 15 or 30 years, and they usually have fixed interest rates.
Auto Loans: An auto loan is a loan used to purchase a vehicle. Like a mortgage, the loan is secured by the vehicle itself, so if the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can repossess the vehicle. Auto loans are typically repaid over a period of 4 to 7 years and usually have fixed interest rates.
Personal Loans: A personal loan is an unsecured loan that can be used for any purpose. Because personal loans are unsecured, they typically have higher interest rates than other types of loans. Personal loans are typically repaid over a period of 2 to 5 years.
Student Loans: A student loan is a type of personal loan that is specifically designed for students who are enrolled in college or university. Student loans usually have lower interest rates than other types of personal loans, and they may offer repayment options that are based on the borrower’s income after graduation.
How the Bank Decides if You’re Eligible for a Loan
The first step in getting a loan from the bank is to fill out a loan application. The loan application will ask for your personal information, employment history, and financial information. The bank will use this information to decide if you’re eligible for a loan and how much they’re willing to lend you.
Your Credit Score
Your credit score is one of the most important factors in whether or not you will be approved for a loan. Lenders use your credit score to determine how likely you are to repay a loan, and the higher your score, the more likely you are to be approved. There are a few things that can affect your credit score:
-Your payment history: Do you always pay your bills on time? Are there any late payments or collections?
-Your credit utilization: This is how much of your available credit you are using. It’s best to keep this number below 30%
-Length of credit history: The longer you’ve been using credit, the better. This shows lenders that you’re a responsible borrower
-Types of credit: A mix of different types of credit (i.e. revolving, installment, etc.) shows that you can manage different types of debt
-Inquiries: Every time you apply for new credit, an inquiry is placed on your report. Too many inquiries in a short period of time can actually lower your score
Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
Understanding your DTI is important because it determines how much of a monthly loan payment you can afford. Lenders will calculate your DTI by adding up all of your monthly debts — including your mortgage, car loans, student loans, credit card payments, and any other reoccurring payments — and divide that number by your gross monthly income.
For example, if you have a monthly mortgage payment of $1,000 and monthly credit card payments of $500, your monthly DTI would be $1,500/$6,000, or 25%.
To give you a better idea of what counts as debt, here are some common examples:
-Housing expenses: Mortgage or rent payments, property taxes, homeowner’s insurance
-Vehicle expenses: Car loan or lease payments, gasoline expenses, vehicle registration
-Childcare expenses
-Student loan payments
-Minimum credit card payments
-Personal loan payments
Your Employment History
One of the first things that a bank will consider when you apply for a loan is your employment history. They will want to see that you have a steady job and that you have been employed for a significant amount of time. They may also consider your salary and whether or not you have any other sources of income. This information will help them to determine if you are a good candidate for a loan and if you will be able to afford the monthly payments.
What to Do if You’re Denied a Loan
If you’ve been denied a loan from the bank, it can be a frustrating experience. You may feel like you’ve been turned down for no good reason. However, there are a few things you can do to try to get the loan you need. In this article, we’ll go over what to do if you’re denied a loan from the bank.
Improve Your Credit Score
If you have been denied a loan, it is important to first check your credit score. There are several things you can do to improve your credit score, including:
-Check your credit report for errors and dispute them
-Pay your bills on time
-Reduce your debt
-Avoid opening new lines of credit
Get a Cosigner
If you’re having trouble getting approved for a loan, one option is to get a cosigner. A cosigner is someone who agrees to sign the loan with you and is equally responsible for making payments. This can be helpful if you have bad credit or no credit history because your cosigner’s good credit can help you get approved.
Keep in mind that a cosigner is taking on a big responsibility. If you miss payments or default on the loan, your cosigner’s credit will be affected. So it’s important to only sign with someone you trust and who is willing and able to make payments if you can’t.
Find a Different Lender
It can be disappointing and frustrating to be denied a loan, especially if you really need the money. But don’t give up – there may be other options.
Here are some things to try if you’re denied a loan:
-Find out why you were denied. The lender should give you a reason for why your loan was denied. It could be due to your credit score, income, debts, or something else. Once you know the reason, you can work on fixing it.
-Look for a different lender. Just because one lender denies your loan doesn’t mean others will. Shop around and compare offers from multiple lenders before making a decision.
-Apply for a different type of loan. There are many different types of loans available, so if you’re denied one type, try applying for a different one. For example, if you’re denied a personal loan, try applying for a credit card or business loan instead.
-Get help from someone else. If you can’t get approved for a loan on your own, someone else may be able to help by cosigning or guaranteering the loan for you. Just keep in mind that this is a big responsibility and should only be done as a last resort.
If you’re still having trouble getting approved for a loan, there are other options to consider, such as borrowing from friends or family, using collateral to get a secured loan, or getting a payday loan (which is not recommended due to the high interest rates).