How Long Does Late Payment Affect Credit Score?
Contents
Find out how long late payments stay on your credit report and how they affect your credit score.
Checkout this video:
The basics of credit scores
A credit score is a number that indicates how likely you are to repay a loan. It is used by financial institutions to decide whether to lend you money, and if so, how much. Your credit score is based on your credit history, which is a record of your borrowing and repayment behaviour. Late payments can have a negative impact on your credit score.
What is a credit score?
A credit score is a number that reflects the likelihood of you paying back a loan. A high score indicates that you’re a low-risk investment; a low score, however, might make it difficult or impossible to qualify for loans, or force you to take on less favorable terms (like higher interest rates).
Credit scores are derived from information in your credit report, which includes data on how much debt you have and your payment history. Payment history makes up 35% of your credit score, so late payments can have a big impact. But the effects of late payments diminish over time, and eventually disappear from your credit report entirely.
We’ll go into more detail on how late payments affect your credit score below. First, though, let’s review the basics of credit scores.
How is a credit score calculated?
Credit scores are calculated using a number of factors, including payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, and more. Payment history is one of the most important factors in credit scores, and late payments can have a significant impact.
Late payments can stay on your credit report for up to seven years, and they can weigh heavily on your score. In general, the more recent the late payment, the more it will impact your score. If you have a history of late payments, you may want to take steps to improve your payment habits before applying for new credit.
Credit utilization is also a important factor in credit scores. This is the amount of debt you have compared to your credit limit. It’s important to keep your credit utilization low, as maxing out your credit cards can indicate to lenders that you’re overextended.
length of credit history is another factor that’s used in calculatingcredit scores. In general, the longer you’ve been borrowing money and making timely payments, the better your score will be. If you have a short credit history, there are a few things you can do to improve your score over time.
Making on-time payments and keeping your debt levels low are two of the most important things you can do to maintain a good credit score. If you have overdue payments or high levels of debt, taking steps to improve your payment history and reduce your debt load can help you improve your score over time.
The effect of late payments on credit scores
How long does a late payment stay on your credit report?
The effect of late payments on credit scores varies depending on how late the payment is and whether it is a missed or partial payment. Generally, the further behind you are on payments, the worse your score will be affected.
If you make a partial payment, most scoring models will consider that a missed payment. However, some newer scoring models may not treat partial payments as harshly.
Payments that are 30 days or more late will typically have the biggest impact on your score. Payments that are 60 days or more overdue will usually result in a more significant drop in your score. And payments that are 90 days or more delinquent can have an even bigger effect.
In general, late payments can stay on your credit report for up to seven years. However, specific rules may apply in certain cases. For example, if you file for bankruptcy, all late payments may be removed from your report after seven years. Or if you enter into a debt management plan, your late payments could be removed after three years.
How long does a late payment affect your credit score?
One common question we get is “how long will a late payment affect my credit score?” The answer, unfortunately, is not as straightforward as we would like.
First, it’s important to understand that there are two different types of late payments: those that are 30 days or more past due, and those that are less than 30 days past due. Both types of late payments can have a negative impact on your credit score, but the effect of a late payment diminishes over time.
A 30-day late payment will have a bigger impact on your credit score than a late payment that is only a few days past due. That’s because the later you are with your payment, the more likely it is that your creditor will report the delinquency to the credit bureaus. And once your creditor reports the late payment to the credit bureaus, it will be reflected in your credit score.
However, even though a 30-day late payment has a bigger impact on your credit score than a late payment that is only a few days past due, both types of late payments will have a negative impact on your score. So if you’re trying to improve your credit score, it’s best to avoid any type of late payment.
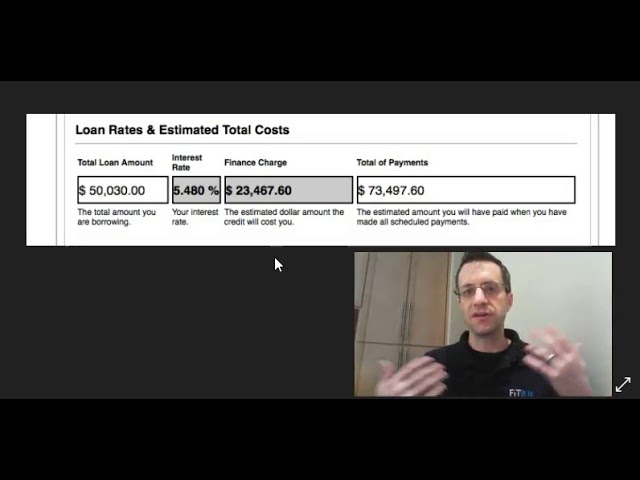
The exact amount that a late payment will affect your credit score depends on several factors, including how late the payment is and how often you makelate payments. But in general, you can expect Late Payment A to drop your score anywhere from 60 to 110 points.
What is the difference between a late payment and a delinquent account?
A late payment is defined as a payment that is 30 days or more past due. A delinquent account is an account that has been turned over to a collection agency. Both late payments and delinquent accounts can have a negative effect on your credit score.
Late payments will remain on your credit report for seven years from the date of the first late payment. Delinquent accounts will remain on your credit report for seven years from the date of the first delinquency.
How to avoid late payments
Set up automatic payments
The best way to avoid making late payments is to set up automatic payments with your creditors. That way, you can be sure that your bills will be paid on time every month. You can also set up alerts with your creditors so that you know when a payment is due.
If you do miss a payment, make sure to contact your creditor as soon as possible. Explain the situation and ask for an extension. Most creditors are willing to work with you if you’re honest and upfront about your situation.
Make a budget
One of the best ways to avoid late payments is to make a budget and stick to it. When you know where your money is going, it’s easier to make adjustments when necessary and ensure that all of your bills are paid on time. If you’re struggling to make ends meet, consider looking for ways to cut costs or increase your income.
Another helpful tip is to set up automatic payments for your bills. That way, you can ensure that the money will be there when it’s time to pay. You can also set up reminders so that you don’t forget to make a payment.
Finally, keep in mind that late payments can have a negative impact on your credit score. If you’re struggling to make payments, contact your creditors as soon as possible to discuss your options.
Prioritize your bills
One way to avoid late payments is to prioritize your bills. This means that you will pay the bills that are most important first. For example, you may want to pay your rent or mortgage first, followed by your utilities, and then your credit card bill. By prioritizing your bills, you can ensure that the most important bills are paid on time, and you can avoid late fees and penalties.
Another way to avoid late payments is to set up automatic payments. This means that your bill will be automatically paid from your bank account each month. This can be a great way to ensure that your bills are always paid on time. You can typically set up automatic payments online or over the phone with your bank or creditor.
If you are having trouble making ends meet, you may also want to consider consolidating your debts. This means taking out a loan to pay off all of your outstanding debts. By consolidation, you can often get a lower interest rate and make one monthly payment instead of multiple payments. However, it is important to carefully consider consolidation before taking out a loan, as it may not be the right solution for everyone.
How to improve your credit score
Your credit score is important. It is used to determine the interest rates you qualify for when you borrow money. A high credit score means you’re a low-risk borrower, which could lead to better loan terms. A low credit score could lead to higher interest rates and could mean you won’t qualify for certain types of loans. So, how can you improve your credit score?
Check your credit report for errors
One of the best ways to improve your credit score is to check your credit report for errors. You can get a free copy of your credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus – Experian, Equifax and TransUnion – once every 12 months.
Look for anything that looks incorrect, such as an account that doesn’t belong to you, late payments that have been paid on time, or incorrect information about your payment history. If you find any errors, dispute them with the credit bureau.
You can also try to improve your credit score by paying down your debts, including any delinquent accounts. The goal is to get your debt-to-credit ratio below 30%, which is considered good. If you can get it below 10%, that’s even better.
Use a credit monitoring service
Credit monitoring services can help you keep track of your credit score and alert you to any changes. Some of these services also offer other features, such as information about loans and credit cards, that can help you make informed financial decisions.
Get a credit counseling or debt management plan
Credit counseling or debt management plans can help you pay off your debt over time. They typically involve working with a counselor to create a budget and come up with a payment plan that works for your unique financial situation.
Debt management plans are offered by credit counseling organizations. They work with your creditors to develop a repayment plan that fits your budget and timeline. These plans usually last three to five years and can help you get out of debt during that time.
If you can’t afford the monthly payments on a debt management plan, you may want to consider credit counseling instead. Credit counseling is a nonprofit service that helps people get out of debt. With credit counseling, you’ll work with a counselor to create a budget and come up with a payment plan that works for your unique financial situation.