Which of the Following Accounts Has a Normal Credit Balance?
Contents
If you’re trying to keep track of your finances, it’s important to know which accounts have a normal credit balance. This will help you stay organized and avoid any surprises. Here’s a quick rundown of which accounts typically have a normal credit balance.
Checkout this video:
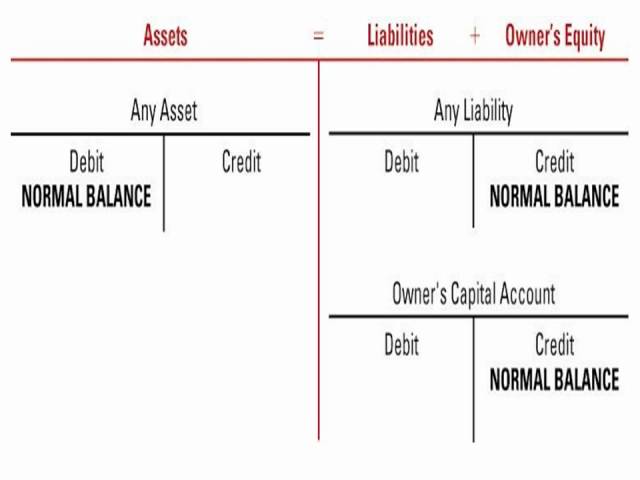
Accounts with Normal Credit Balances
There are several types of accounts in accounting, but only a few have normal credit balances. The most common account with a normal credit balance is the asset account. This is because when an asset is purchased, it is recorded as a credit.
Accounts Receivable
In double-entry bookkeeping, Accounts Receivable (A/R) is regarded as a liability, since it represents money owed by the company to its creditors (i.e., customers). Accounts Receivable are therefore recorded as a current liability on the company’s balance sheet.
In most cases, the Accounts Receivable account has a normal credit balance, meaning that when it is closed at the end of an accounting period, any remaining balance is carried over to the next period as a credit.
Inventory
In accounting, inventory refers to all the goods and materials that a company has on hand to sell. For instance, if you own a clothing store, your inventory would include all the clothes, shoes, and accessories that you have in stock. Inventory is considered an asset of a company because it can be sold for cash.
In bookkeeping, assets are categorized as either “real” or “personal.” Real assets are things like land and buildings—things that can’t be moved. Personal assets are everything else, including inventory. Because inventory is an asset that can be turned into cash, it has a “normal” credit balance. That means when you add up all the credits and debits for inventory, the total should be a credit.
Prepaid Expenses
Prepaid expenses are paid in advance and reported on the balance sheet as assets. These payments are for goods or services that will be used in the future and need to be recorded as an asset to comply with the matching principle. Unlike other types of assets, such as cash or accounts receivable, prepaid expenses usually have a lifespan of one year or less. Examples of prepaid expenses include:
-Prepaid insurance
-Prepaid rent
-Prepaid advertising
Other Current Assets
Other Current Assets may include:
-unbilled revenues
-prepaid expenses
-short-term investments
-deferred tax assets
Accounts with Normal Debit Balances
The following is a list of accounts that normally have a debit balance: Accounts Receivable, Cash, Common Stock, Service Revenue.
Accounts Payable
Accounts Payable (A/P) is an account that represents the money you owe to your suppliers for goods and services purchased on credit. A/P is a liability because it represents money you will eventually have to pay back.
There are two types of A/P accounts: trade credit and nontrade credit. Trade credit is given by suppliers to their regular customers for the purchase of inventory. Nontrade credit is given by companies to cover expenses such as utilities, rent, and insurance premiums.
Your A/P balance will usually be a debit, but it can also be a credit if you have overpaid your suppliers. An A/P debit occurs when the amount you owe to your supplier (the liability) is greater than the amount of trade credit you have been extended. An A/P credit occurs when the amount of trade credit you have been extended (the asset) is greater than the amount you owe to your supplier.
Wages Payable
Wages payable is an account that represents the amount of money that an employer owes to its employees for work that has been completed but not yet paid for. This account typically has a credit balance, which means that the amount of money owed to employees is increasing.
Interest Payable
Interest payable is an account that typically has a credit balance. This account represents the interest accrued on a loan or other debt that has not yet been paid. The amount of interest that accrues on a debt is based on the interest rate and the length of time that the debt is outstanding.
Taxes Payable
The balance in the Taxes Payable account is a credit if the amount of taxes owed by the company is less than the amount of taxes paid by the company. The normal balance for the Taxes Payable account is a credit.
Accounts with Mixed Credit and Debit Balances
Trying to determine which of your accounts has a normal credit balance can be confusing, especially if you have multiple accounts with mixed credit and debit balances. In this article, we’ll break down the credit balance definition and give you some tips on how to identify which of your accounts has a normal credit balance.
Common Stock
Common stock is a type of investment that represents ownership in a corporation. If the corporation does well, the value of the stock goes up and shareholders can make money. If the corporation does poorly, the value of the stock goes down and shareholders can lose money.
The majority of corporations are owner-operated, meaning that they are owned by the people who run them. For these types of businesses, common stock is not an issue because there is no need to raise money from outside investors. But for other types of businesses, such as public companies, common stock is a way to raise money from investors.
Common stock is also a way for investors to share in the profits of a company. When a company makes money, it can choose to distribute some of its profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. Dividends are payments made by a corporation to its shareholders. They are usually paid out quarterly (every three months).
Not all companies choose to pay dividends, but for those that do, dividend payments can be a significant source of income for shareholders.
Dividends
Dividends are account balances that a company’s board of directors has voted to pay out to shareholders. A company may choose to pay dividends in cash or issue new shares of stock. Dividends are normally paid out quarterly, but some companies pay them semiannually or annually.
Dividends are not an expense on the company’s income statement. Instead, they are a distribution of the company’s earnings. The income statement includes an item called “retained earnings,” which is the portion of earnings that the company has not paid out in dividends.
There are two types of dividends:
-Cash dividends: These are payments made in cash (usually from the company’s checking account) to shareholders. Cash dividends are taxable as personal income to the shareholders.
-Stock dividends: These are payments made in shares of stock to shareholders. Stock dividends are not taxable as income to the shareholders.
Service Revenue
Service revenue is earned when we provide a service to customers. This can be in the form of professional services, consulting, or other types of work. Service revenue is recognized when the service is performed, and it is reported on the income statement in the period when it is earned.
Accounts that have mixed credit and debit balances are those where some transactions will increase the balance and some will decrease it. An account with a normal credit balance will always have more credits than debits. The following accounts typically have mixed balances:
-Sales
-Revenue
-Expenses
Interest Revenue
Interest revenue is generated when a company loans money to another party and charges interest on the loan. The terms of the loan will dictate when interest payments must be made, and the amount of interest that must be paid. The company receiving the loan will make periodic payments to the lender, which will include both the principal amount of the loan and the interest charges.
The balance in the interest revenue account represents the amount of money that a company has earned from lending money to others. This account will usually have a credit balance, since it represents income for the company.