How Does a Bank Loan Work?
Contents
How Does a Bank Loan Work? You may be wondering how does a bank loan work? Banks make money by loaning it out to people and businesses. The borrower pays the bank back over time, usually with interest.
Checkout this video:
Introduction
A bank loan is a type of debt financing provided by banks to help individuals or businesses finance their activities. Bank loans are typically structured as either term loans or lines of credit. Term loans are typically used for specific projects or one-time expenses, such as expanding a business or buying real estate. Lines of credit, on the other hand, may be used for ongoing expenses, such as working capital or inventory financing.
How Does a Bank Loan Work?
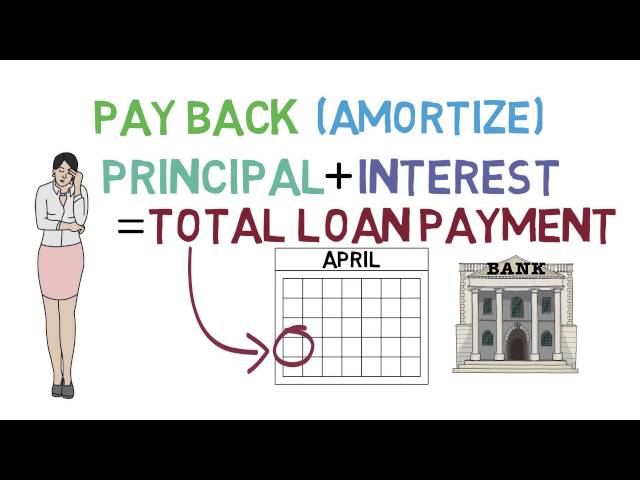
A bank loan is a type of credit that allows you to borrow money from a financial institution and then pay it back over time. This type of credit can be used for a variety of purposes, including buying a car, consolidating debt, or financing a large purchase. When you take out a bank loan, you will typically be required to make regular payments until the loan is paid off.
Applying for a loan
When youapply for a loan, the bank will check your credit score to help them decide if they will approve your loan and how much interest to charge you. If you have a good credit score, you’re more likely to get approved for a loan and pay a lower interest rate.
The bank will also look at your income and debts to decide how much money to lend you and if you can afford the monthly payments. If you have a lot of debt, the bank may not approve your loan or may only lend you a small amount of money.
The loan process
When you take out a loan from a bank, you are borrowing money that you will need to pay back, with interest. The bank will review your financial history and credit score to determine how much money they are willing to loan you and at what interest rate. Once you have been approved for the loan, you will sign a contract stating the terms of the loan, including the amount borrowed, the interest rate, the repayment schedule, and any fees or penalties associated with the loan.
You will then begin making monthly payments on the loan until it is paid off in full. Your payments will go towards both the principal (the amount borrowed) and the interest. The higher your interest rate, the more of your payment that will go towards interest rather than towards paying off the principal.
If you default on your loan, meaning you miss one or more payments, the bank may take steps to collect on the debt. This could include sending your account to a collections agency or even taking legal action against you. Defaulting on a loan can damage your credit score and make it difficult to get approved for future loans.
Types of loans
Most banks offer two types of loans: short-term and long-term. Short-term loans are typically for smaller amounts of money and have a shorter repayment period than long-term loans. Long-term loans are usually for larger amounts of money and have a longer repayment period.
Conclusion
A bank loan is a form of credit that allows you to borrow money from a lender and then pay it back over time. There are many different types of bank loans, but the most common is a personal loan.
When you take out a personal loan, the lender will give you a set amount of money that you can use for any purpose. You will then have a set period of time to repay the loan, usually between one and five years. The interest rate on a personal loan is usually fixed, which means it will not change over the life of the loan.
If you are thinking about taking out a bank loan, it is important to understand how they work and what the terms and conditions are. You should also shop around to get the best interest rate and repayment plan for your needs.