How Does a Loan from a Bank Work?
Contents
A bank loan is when a bank gives you money that you will need to pay back with interest. The interest is the price you pay for borrowing the money. Most people take out loans to buy things like a car or a house.
Checkout this video:
What is a loan from a bank?
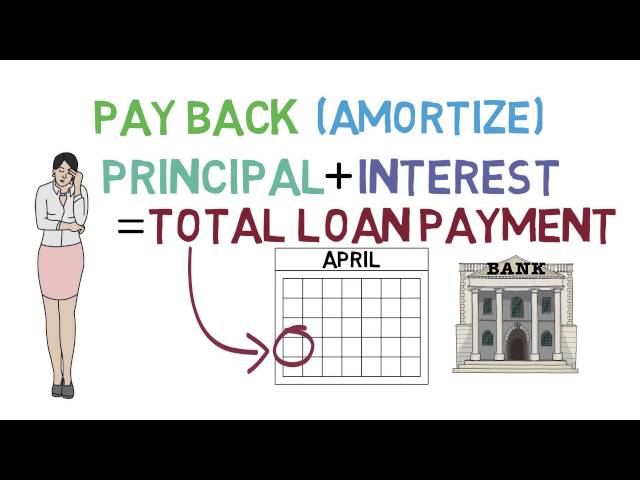
A loan from a bank is a financial product that allows you to borrow money from a lender and then repay it over time. The lender may be a traditional bank, credit union, or online lender.
The loan process usually starts with an application, followed by a credit check and, if approved, the disbursement of funds. Loan terms vary, but most loans have a fixed interest rate and repayment period.
Repayment typically occurs monthly and may be made via automatic withdrawals from your checking account or through online bill pay. Some loans may require collateral, such as a car or home equity, to secure the loan.
Loans can be used for a variety of purposes, such as to consolidate debt, finance a large purchase, or cover unexpected expenses. Depending on the reason for the loan, there may be specific qualifications you need to meet in order to be approved.
How does a loan from a bank work?
A bank loan is when a bank gives you money that you borrow and then pay back with interest. The interest is how the bank makes money from loaning you money. There are different types of bank loans, but most work the same way. You fill out an application, the bank approves you, and then you get the money and start paying it back.
The borrower applies for a loan from the bank
The borrower applies for a loan from the bank by filling out a loan application. The application will ask questions about the borrower’s income, employment history, and debts. The borrower will also have to provide financial documents, such as tax returns and pay stubs, to support their loan application.
Once the application is complete, the bank will review it to see if the borrower qualifies for the loan. If they do, the bank will send them a loan offer, which will include information about the interest rate, repayment terms, and fees associated with the loan. The borrower can then choose to accept or reject the loan offer.
The bank reviews the borrower’s application and credit history
The first step in applying for a loan from a bank is to complete a loan application. The loan application will ask for information about your income, employment history, monthly expenses, debts, and assets. The bank will also pull your credit report to get a better understanding of your credit history.
After reviewing the borrower’s application and credit report, the bank will make a decision about whether or not to approve the loan. If the loan is approved, the borrower will be notified of the loan amount, interest rate, and repayment terms. The borrower will then need to sign the loan agreement and begin making monthly payments.
The bank approves the loan and the borrower receives the money
After the bank approves the loan, the borrower will receive the money. They will then need to make monthly payments to the bank in order to pay back the loan, plus interest.
The borrower repays the loan with interest
In order to get a loan from a bank, the borrower must first fill out an application. The application will ask for information about the borrower’s employment, income, and debts. The bank will use this information to determine whether or not the borrower is a good candidate for a loan.
If the borrower is approved for a loan, they will be given a set amount of money that they will need to repay, plus interest. The interest rate will be based on the borrower’s credit score and the length of the loan. The borrower will need to make monthly payments until the loan is paid off in full.
What are the benefits of a loan from a bank?
There are several benefits of taking out a loan from a bank. One benefit is that banks usually offer loans with lower interest rates than other lenders, such as credit unions or online lenders. This means you’ll save money on interest over the life of your loan.
Another benefit of a bank loan is that you’ll likely have more time to repay the debt than you would with other types of loans. For example, personal loans typically have repayment terms of two to five years, while mortgage loans may have repayment terms of 15 or 30 years. This means you can better manage your finances and budget for the long term.
finally, banks are regulated by federal and state laws, which offer protections for borrowers. For example, the Truth in Lending Act requires lenders to disclose the cost of borrowing, including the annual percentage rate (APR), before you agree to take out a loan. This helps you know exactly how much your loan will cost and compare offers from different lenders.